Drones, referred to as unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), are flying devices that can either be remotely controlled or fly autonomously and come in various shapes and sizes with features like propulsion systems for flight, navigation systems for control, task-specific payloads, and an operation control system. They have a wide range of applications, from aerial photography and videography, delivery, mapping and surveying, agriculture, environmental monitoring, rescue operations, law enforcement to military and defense. However, as technology improves and drones become more versatile, their use raises privacy and safety concerns leading to regulations in many countries to govern their usage.
What are Surface and Underwater Drones?

Surface drones, also known as ground drones, are unmanned aerial vehicles that operate on land or water surfaces. They are used for tasks such as inspection, surveying, mapping, delivery, search and rescue, and security operations and come in various shapes and sizes, with features like navigation systems, propulsion systems, and payloads for specific tasks.
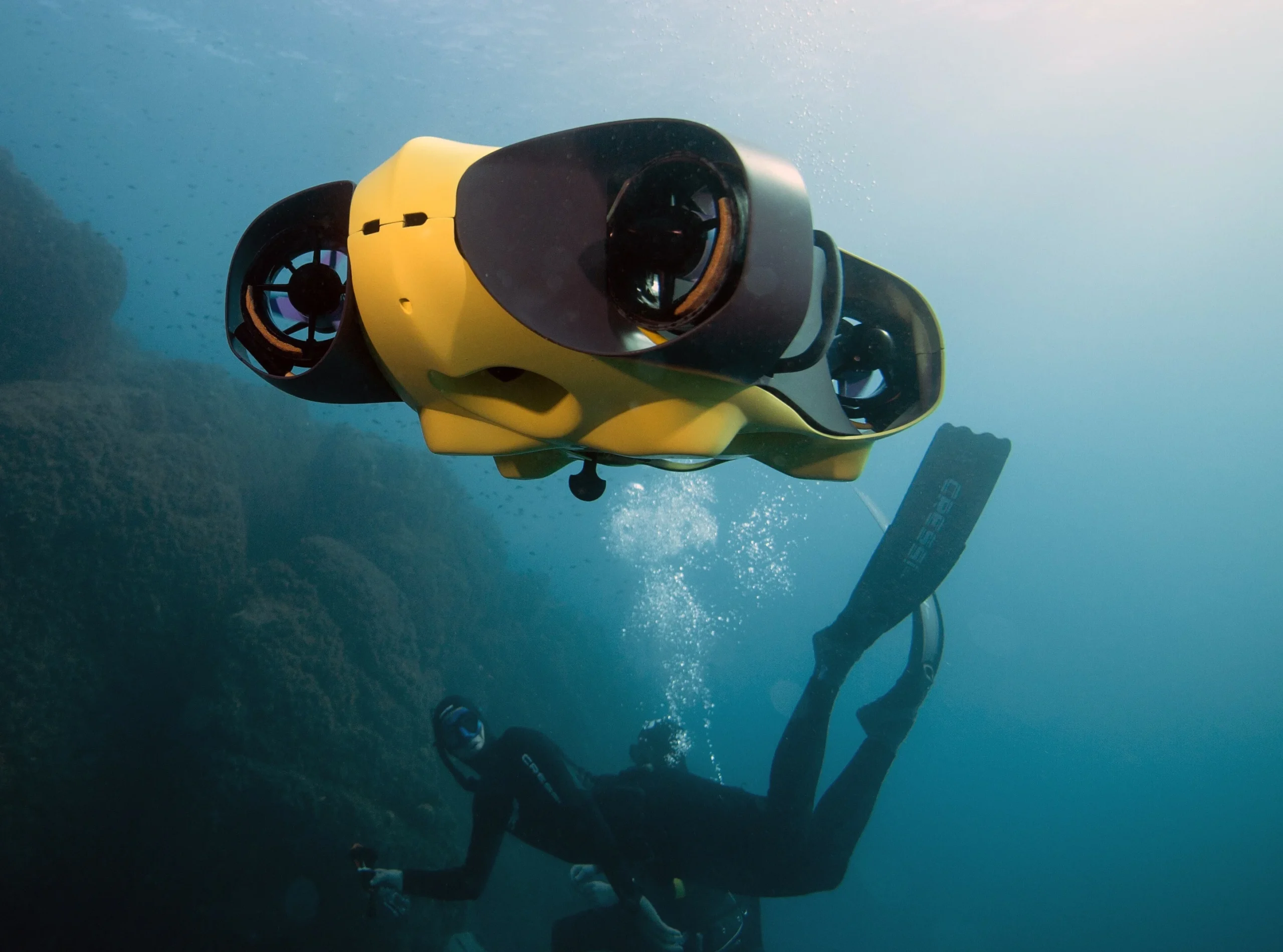
On the other hand, underwater drones, also referred to as underwater remotely operated vehicles (ROVs) or underwater autonomous vehicles (UAVs), are underwater robots that can be controlled remotely or operate autonomously. Equipped with cameras, lights, and other sensors, they are used for tasks such as underwater exploration, inspection, surveying, and monitoring in various environments, including lakes, oceans, and rivers. They come in various shapes and sizes and are designed to manoeuver in the underwater environment and communicate with the operator on the surface.
Features of Surface and Underwater Drones
Following are the various features and properties of both surface and underwater drones.
Surface Drones:
- Navigation systems for precise control and movement
- Propulsion systems for movement on land or water
- Payloads for specific tasks, such as cameras, lights, and sensors
- Remote control or autonomous operation
- Durable construction for outdoor use
- Communication systems for real-time data transfer
Underwater Drones:
- Waterproof housing for underwater operations
- Propulsion systems for underwater movement
- Navigation systems for precise control and movement
- Equipment such as cameras, lights, and sensors for gathering data
- Communication systems for real-time data transfer
- Autonomous or remote control operation
- Manoeuvrability in the underwater environment
- Depth control systems for diving to specific depths.
Applications of Surface and Underwater Drones
Following are the various applications and uses of both surface and underwater drones.
- Inspection of infrastructure such as bridges and buildings
- Surveying and mapping land and water surfaces
- Delivery of packages and supplies
- Search and rescue operations
- Security and surveillance
- Environmental monitoring
- Agriculture and farming

Underwater Drones:
- Underwater exploration and research
- Inspection and maintenance of underwater structures
- Surveying and mapping of the ocean floor
- Monitoring marine life and aquatic environments
- Search and rescue operations
- Salvage and recovery of sunken ships and artifacts
- Environmental monitoring and monitoring of oceanic oil rigs.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Surface drones
Advantages of Surface Drones:
- Efficiency: Drones can cover large areas quickly and efficiently, reducing the time and effort required for manual inspections and surveys.
- Cost-effectiveness: Drones are often less expensive than traditional methods and do not require human operators, reducing the cost of labor.
- Accessibility: Drones can access difficult-to-reach areas and environments, making it easier to gather data and information.
- Safety: By using drones, hazardous tasks can be performed without putting human operators in harm’s way.
- Precision: Drones can be equipped with high-quality cameras, sensors, and navigation systems, allowing for precise data collection and control.
Disadvantages of Surface Drones:
- Privacy concerns: The use of drones for surveillance or data collection can raise privacy concerns for individuals and communities.
- Limited battery life: Drones typically have limited battery life, limiting their range and duration of use.
- Weather restrictions: Drones can be affected by inclement weather, such as strong winds and rain, making it difficult or impossible to operate.
- Regulatory restrictions: In some countries, there may be restrictions or regulations on the use of drones for commercial or personal purposes, limiting their availability and use.
- Technical difficulties: Drones require technical expertise to operate and maintain, and can be expensive to repair if damaged.
Underwater drones
Advantages of Underwater Drones:
- Accessibility: Drones can access difficult-to-reach underwater environments, making it easier to gather data and information.
- Safety: By using drones, hazardous underwater tasks can be performed without putting human divers in harm’s way.
- Precision: Drones can be equipped with high-quality cameras, sensors, and navigation systems, allowing for precise data collection and control.
- Cost-effectiveness: Drones are often less expensive than traditional methods, such as manned submersibles, and do not require human divers, reducing the cost of labor.
- Efficiency: Drones can cover large areas quickly and efficiently, reducing the time and effort required for manual inspections and surveys.

Disadvantages of Underwater Drones:
- Limited battery life: Drones typically have limited battery life, limiting their range and duration of use.
- Technical difficulties: Drones require technical expertise to operate and maintain, and can be expensive to repair if damaged.
- Limited communication: Communication can be limited underwater, making it difficult to transmit real-time data and control the drone.
- Weather restrictions: Drones can be affected by water conditions, such as currents and visibility, making it difficult or impossible to operate.
- Regulatory restrictions: In some countries, there may be restrictions or regulations on the use of underwater drones for commercial or personal purposes, limiting their availability and use.
Uses in Specific Industries
Surface drones
Surface Drones in Various Industries:
- Agriculture: Drones are used for crop mapping and monitoring, irrigation management, and plant health analysis.
- Construction: Drones are used for surveying, site inspections, and 3D modeling of building and infrastructure projects.
- Delivery: Drones are used for delivery of packages, medical supplies, and food to remote or hard-to-reach areas.
- Energy: Drones are used for inspections of wind turbines, solar panels, and pipelines, as well as monitoring environmental impact and wildlife populations.
- Environmental monitoring: Drones are used for monitoring wildlife populations, deforestation, and natural disaster response.
- Film and Media: Drones are used for aerial photography and videography, providing unique perspectives for movie production and news coverage.
- Law Enforcement: Drones are used for surveillance, search and rescue operations, and crowd control.
- Mining: Drones are used for surveying and mapping mines, as well as monitoring environmental impact and wildlife populations.
- Real Estate: Drones are used for property inspections, marketing and advertising, and aerial photography.

Underwater drones
Underwater Drones in Various Industries:
- Aquaculture: Drones are used for monitoring and managing fish farms, and for inspecting underwater structures and equipment.
- Environmental monitoring: Drones are used for monitoring underwater ecosystems, tracking marine species, and collecting data on water quality and pollution levels.
- Energy: Drones are used for inspecting underwater pipelines, oil rigs, and other energy infrastructure.
- Geology and Mining: Drones are used for mapping underwater mineral deposits, collecting core samples, and performing geological surveys.
- Law enforcement: Drones are used for monitoring illegal fishing, detecting underwater smuggling and trafficking, and supporting search and rescue operations.
- Oceanography: Drones are used for exploring the deep sea, collecting oceanographic data, and studying underwater geological features.
- Search and Rescue: Drones are used for searching and locating sunken ships, aircraft, and other underwater objects.
- Shipping and Port Operations: Drones are used for inspecting underwater structures, such as ships, piers, and ports, and for monitoring underwater security and environmental impact.
Comparison between Surface and Underwater Drones
Following is a comparative table between surface and underwater drones.
| Feature | Surface drones | Underwater drones |
| Environment | Air | Water |
| Movement | Vertical takeoff and landing | Move through water |
| Payload | Cameras, sensors etc. | Specialised payloads for data collection and exploration |
| Navigation | GPS, other navigation systems | Sonar, underwater navigation systems |
| Control | Remote pilot or autonomous | Remote pilot or autonomous |
| Power | Batteries | Batteries or electric propulsion |
| Communication | Wireless | Underwater acoustic modems or tethered communication |
| Cost | Low-cost to expensive | Low-cost to expensive |
Market Value and Demand

The drone market has been rapidly growing and is expected to reach a market size of over $11 billion by 2025. This growth can be attributed to the increased demand for drones in a variety of industries such as agriculture, construction, energy, environmental monitoring, delivery, and photography. The diverse range of applications for drones has been a major driving factor behind this growing demand. These applications range from aerial photography and videography, to delivery, surveying and mapping, agriculture, environmental monitoring, search and rescue operations, law enforcement, and military and defense.
While the demand for drones continues to grow, there are also regulations in place in many countries aimed at addressing privacy and safety concerns. These regulations may impact the future growth of the drone market. Despite these regulatory challenges, technology is improving, making drones more versatile and capable, leading to new uses and innovations in the drone market.
The drone market is highly competitive, with many companies offering a range of drone products and services. These offerings range from low-cost hobbyist models to expensive industrial-grade systems, providing consumers with a wide range of options to choose from. As the demand for drones continues to grow, the drone market is expected to become even more competitive, with new innovations and offerings being introduced to meet this demand.

Companies manufacturing Surface and Underwater Drones
Companies Manufacturing Surface Drones:
- DJI – a Chinese technology company that is the market leader in consumer and professional drones.
- Parrot – a French company that designs, develops, and sells consumer drones and other high-tech products.
- Yuneec – a Chinese company that designs and manufactures consumer and professional drones, electric aircraft, and eVTOLs (electric vertical takeoff and landing aircraft).
- Autel Robotics – a Chinese technology company that designs and manufactures consumer and professional drones for aerial photography, surveying, mapping, and inspection.
- PowerVision – a Chinese technology company that designs, develops, and sells consumer and professional drones for aerial photography, videography, and other applications.
Companies Manufacturing Underwater Drones:
- Ocean Aero – a US company that designs and manufactures underwater drones for ocean exploration, environmental monitoring, and other applications.
- Deep Trekker – a Canadian company that designs and manufactures underwater drones for underwater inspections, surveys, and ocean exploration.
- SubC Partner – a Norwegian company that designs and manufactures underwater drones for subsea inspections, surveys, and monitoring.
- VideoRay – a US company that designs and manufactures underwater drones for a range of applications, including inspections, surveys, and research.
- Kraken Robotics – a Canadian company that designs and manufactures underwater drones and related technology for defense, energy, and oceanographic research.
Conclusion
In conclusion, drones, also known as unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), have revolutionized the way we approach a wide range of tasks, including aerial photography, delivery, surveying, agriculture, environmental monitoring, search and rescue, law enforcement, and military and defense. The versatility of drones has made them popular in many industries, leading to a growing demand for these devices. The drone market is estimated to reach over $11 billion by 2025, which is a testament to the growing popularity of drones.
However, while the demand for drones is growing, it is important to consider the potential privacy and safety concerns that come with their use. To address these concerns, many countries have implemented regulations to govern the usage of drones, which may impact the growth of the drone market in the future. Despite these challenges, the drone market remains highly competitive, with many companies offering a range of drone products and services, ranging from low-cost hobbyist models to expensive industrial-grade systems.
As technology continues to improve, drones are becoming more versatile and capable, leading to new uses and innovations in the drone market. It is clear that drones will play an increasingly important role in our lives as technology advances. However, it is important to consider the potential impact of drones on privacy and safety and to address these concerns with regulations and best practices.