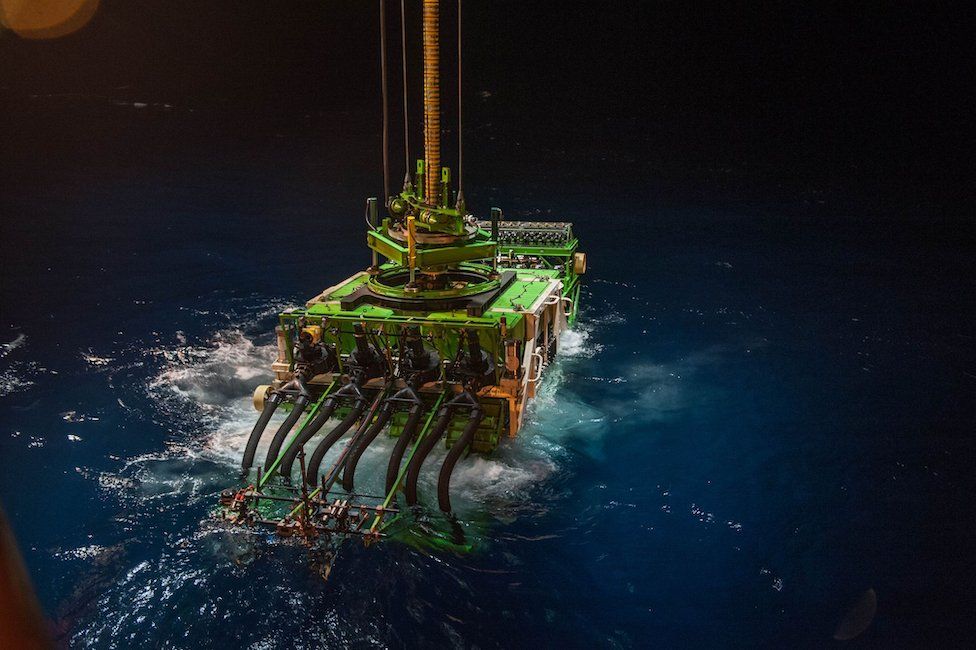
Subsea mining is a complex and technologically advanced method of extracting valuable minerals and resources from the ocean floor. The process involves the use of specialized equipment and technology to extract minerals from the seabed, which is located thousands of meters below the surface of the ocean. Unlike conventional mining techniques, it is performed in deep-sea environments that are beyond the reach of these traditional methods.
There are a variety of minerals and resources that can be extracted through this method, including precious metals such as gold and silver, as well as copper, manganese, and zinc. The primary challenge is to extract these minerals in a manner that is both safe and environmentally responsible, while also ensuring that the process is economically viable.
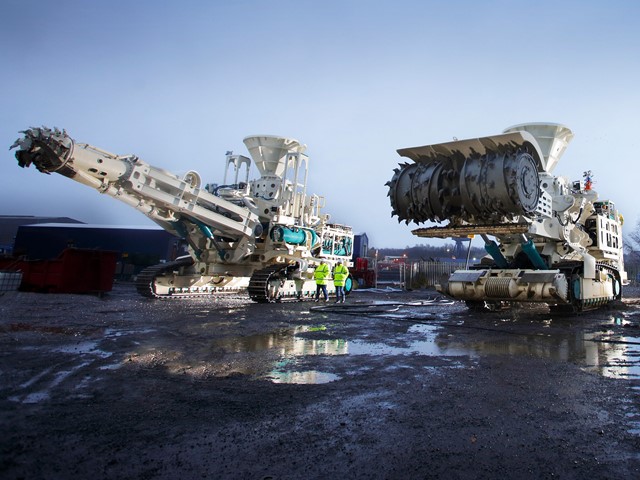
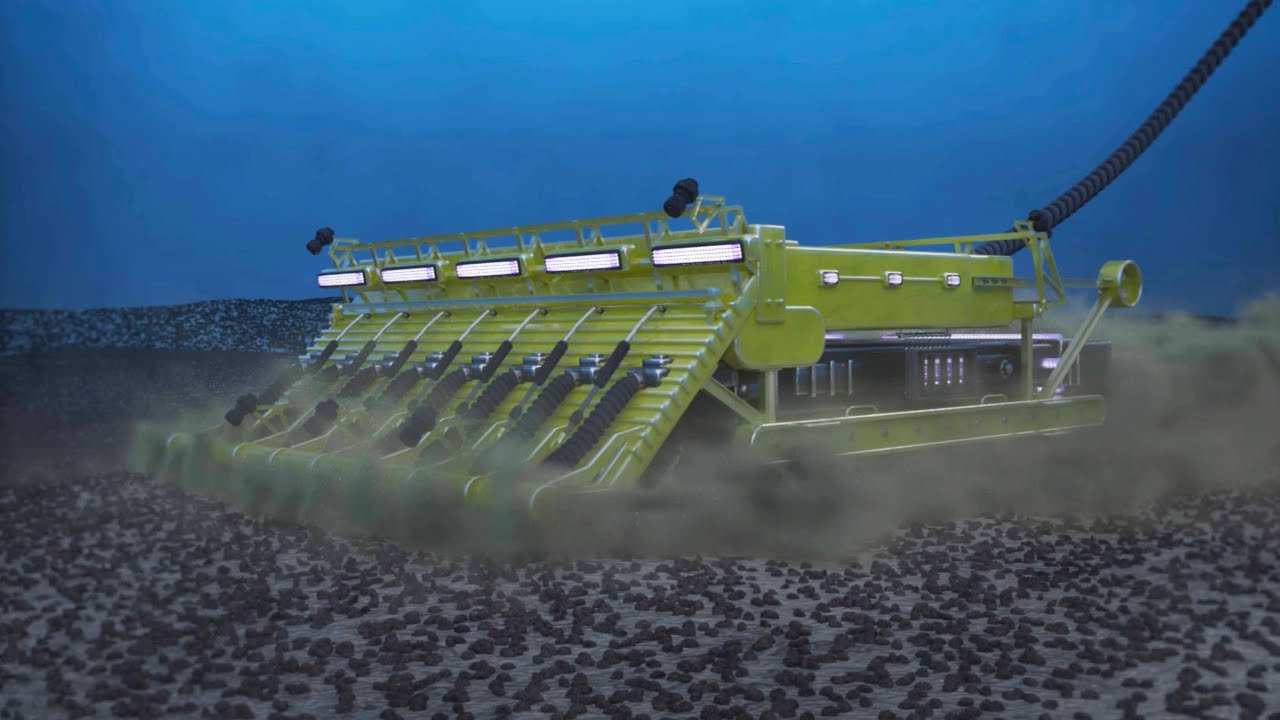
To achieve these goals, a variety of technologies and approaches are utilised. This can include the use of remotely operated vehicles (ROVs) to perform the mining operations, submersible robots that can operate in the deep-sea environment, and specialized mining tools that are designed specifically for this type of extraction. By utilising these tools and technologies, this particular mining can be performed in a way that minimises the impact on the ocean environment while still allowing for the extraction of valuable minerals.
Features
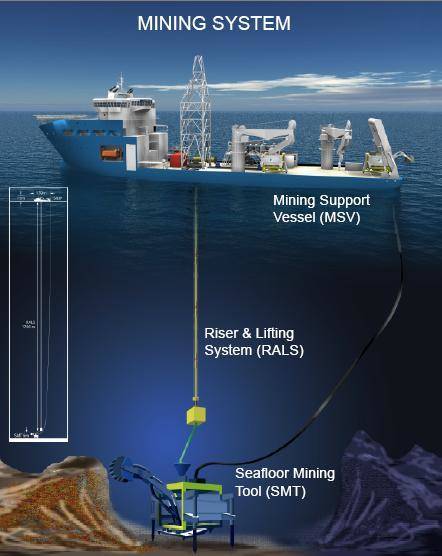
Subsea mining is a highly specialized and technologically advanced form of mining that is characterized by several key features:
- Deep-Sea Environment: It takes place in deep-sea environments that are beyond the reach of conventional mining techniques. This means that the process must be designed to withstand the extreme pressures and challenging conditions of the deep ocean.
- Specialised Equipment: It requires the use of specialised equipment and technology to extract minerals from the ocean floor. This can include remotely operated vehicles (ROVs), submersible robots, and specialized mining tools. These tools and technologies must be designed to operate effectively in the deep-sea environment.
- Resource Extraction: The minerals and resources extracted through subsea mining can include precious metals such as gold and silver, as well as copper, manganese, and zinc. The exact minerals and resources that are targeted will depend on the location and the characteristics of the deposit being mined.
- Environmental Considerations: Subsea mining must be performed in a manner that is environmentally responsible. This means taking steps to minimize the impact of the mining operations on the ocean environment, such as carefully managing the discharge of mining waste and effluent.
- Economic Viability: Subsea mining must also be economically viable in order to be sustainable. This requires carefully managing costs and ensuring that the process is profitable in the long term.
Overall, subsea mining is a highly specialized and technologically advanced form of mining that requires careful consideration of a range of factors in order to be successful. By utilizing the right equipment and technologies, and by taking a responsible approach to environmental management, it is possible to extract valuable minerals and resources from the ocean floor while minimizing the impact on the ocean environment.
Uses
Subsea mining involves the extraction of valuable minerals and resources from the ocean floor for use in various industries. These minerals have numerous applications and play an important role in modern society.
Jewelry and Precious Metals: Precious metals like gold and silver are among the minerals that can be extracted through subsea mining. These metals are highly valued for their rarity and beauty and are used in the manufacture of jewelry, coins, and other luxury goods. The high demand for these metals has led to an increase in subsea mining operations in recent years, as this form of mining provides access to previously untapped reserves of these valuable resources.
Electronics and Telecommunications: Copper and manganese are two minerals that are commonly extracted through subsea mining and used in the production of electronics and telecommunications equipment. Copper, for example, is an essential component in the production of electrical wiring and other electrical components, while manganese is used in the production of steel and other alloys. By extracting these minerals from the ocean floor, subsea mining helps to meet the growing demand for these resources in these industries.

Construction: Copper, zinc, and other minerals extracted through subsea mining play a critical role in the construction industry. These minerals are used in the production of plumbing and electrical systems, as well as in other building materials and components. By providing access to these resources, subsea mining helps to support the ongoing growth and development of the construction industry.
Energy Production: Manganese nodules, which are commonly found on the ocean floor, contain valuable minerals that are used in the production of energy and batteries. Manganese, for example, is used as an additive in the production of steel and alloys, while cobalt and nickel, which are also found in these nodules, are critical components in the production of batteries for electric vehicles and other energy storage applications.
Medical Applications: Some of the minerals extracted through subsea mining, such as silver, have antimicrobial properties and are used in medical and dental applications. Silver, for example, is used in wound dressings, bandages, and other medical products due to its antimicrobial properties. It is also used in dental fillings and other dental applications for the same reason.
In conclusion, subsea mining provides access to a wide range of minerals and resources that are essential for modern life. These minerals play a critical role in supporting various industries, from construction and energy production to electronics and telecommunications. By extracting these resources from the ocean floor, subsea mining helps to meet the growing demand for these minerals and supports the ongoing growth and development of society.
Advantages
Advantages :
- Access to Previously Untapped Resources: Subsea mining provides access to valuable minerals and resources that are located on the ocean floor and were previously inaccessible due to the depth of the water and difficulty of reaching these resources. The ability to access these resources can increase the availability of minerals and resources needed for various industries, helping to meet the growing demand.
- Reduced Environmental Impact: Subsea mining has a smaller environmental footprint compared to traditional surface mining methods. The ocean floor is a largely undisturbed ecosystem, and subsea mining operations can be designed to minimize their impact on the surrounding marine environment. This can include measures such as using remotely operated vehicles to extract minerals, reducing the need for physical access to the site and minimizing the release of sediment and other materials into the ocean.
- Improved Safety: Subsea mining eliminates the need for workers to physically enter mines, reducing the risk of accidents and other safety hazards associated with traditional surface mining methods. This can lead to a safer working environment for those involved in subsea mining operations.
- Cost-Effective: Subsea mining can be more cost-effective than traditional surface mining methods, as it eliminates the need for expensive infrastructure such as roads, railways, and other transportation systems to access remote mining sites. This can result in reduced costs for subsea mining operations, making the extraction of minerals from the ocean floor more economically feasible.
In conclusion, subsea mining has several advantages including access to previously untapped resources, reduced environmental impact, improved safety, and cost-effectiveness. However, it also presents technical and regulatory challenges that must be overcome to make subsea mining a viable option for extracting minerals and resources from the ocean floor.
Disadvantages

Disadvantages :
Technical Challenges: The technical challenges involved in subsea mining are significant and can result in higher costs. Specialized equipment and technology is required to extract minerals from the ocean floor, which can be complex and expensive to operate. In addition, the deep-sea environment presents unique challenges, such as extreme pressures and limited visibility, that require specialized technology to overcome.
Environmental Concerns: Despite the reduced environmental impact compared to traditional surface mining methods, subsea mining still has the potential to harm the marine environment. The extraction of minerals and resources from the ocean floor can disturb delicate ecosystems, and the release of sediment and other materials into the ocean can have negative impacts on marine life, such as causing harm to marine species and altering ocean currents.
Regulatory and Approval Process: The approval process for subsea mining operations is highly regulated and can be lengthy and expensive. New subsea mining operations are subject to intense scrutiny from environmental groups and other stakeholders, and may require extensive environmental assessments and mitigation measures to minimize potential harm to the marine environment.
Economic Feasibility: The high costs associated with subsea mining equipment and technology, as well as the challenges of extracting minerals from the ocean floor, can make subsea mining operations less economically viable than traditional surface mining methods. The profitability of subsea mining operations is also dependent on the availability and prices of minerals and other resources, which are subject to market fluctuations and can impact the feasibility of these operations. In addition, the limited number of subsea mining companies and the small scale of subsea mining operations can also impact their economic viability.
Market and Economic Value
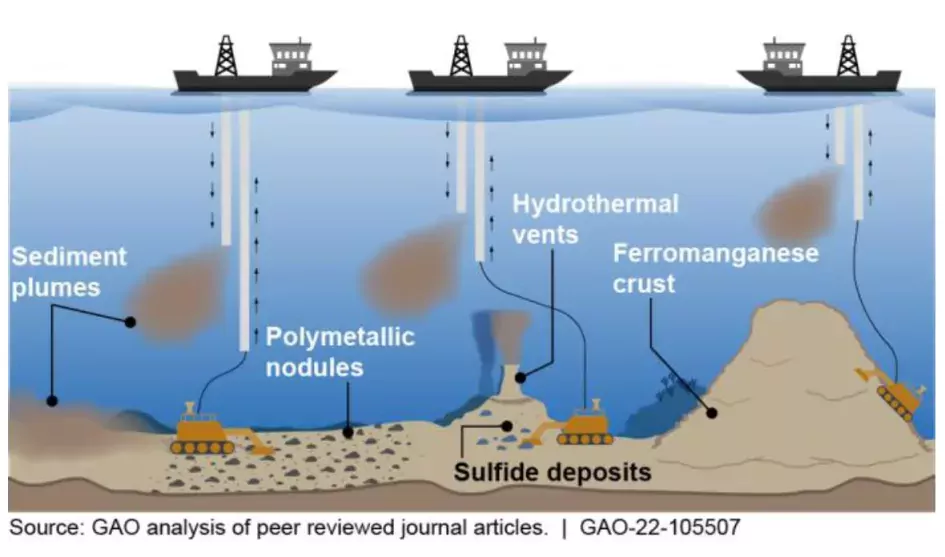
The market and economic value of subsea mining depend on several factors, including the demand for minerals and other resources, the availability of these resources, and the prices at which they can be sold.
Minerals such as copper, manganese, and zinc, which are commonly extracted through subsea mining, are in high demand for use in a wide range of industries, including electronics and telecommunications, construction, and energy production. This demand has driven up the prices of these minerals, making subsea mining more economically viable.
The cost of subsea mining operations, however, can be substantial, due to the need for specialized equipment and technology to extract minerals from the ocean floor. The cost of this equipment and technology, as well as the ongoing operational costs of subsea mining, can impact the profitability of subsea mining operations.
In addition to these economic factors, the development of subsea mining operations is subject to intense scrutiny and regulation, which can result in additional costs and delays. This, combined with the technical challenges of extracting minerals from the ocean floor, can make subsea mining a less economically viable option compared to traditional surface mining methods.
Overall, the market and economic value of subsea mining will depend on a variety of factors, including the demand for minerals and resources, the cost of subsea mining operations, and the availability and prices of these resources.
Conclusion
In conclusion, subsea mining has the potential to play a significant role in meeting the growing demand for minerals and resources that are essential for modern life. However, it is also a challenging and highly regulated industry that presents a number of technical, environmental, regulatory, and economic challenges. Despite these challenges, it offers several advantages, including access to previously untapped resources, reduced environmental impact, improved safety, and cost-effectiveness compared to traditional surface mining methods.
The economic value of subsea mining is dependent on a variety of factors, including the availability and prices of minerals and resources, the cost of equipment and technology, and the regulatory and approval process for its operations. The market for it is likely to continue to grow in the coming years as demand for minerals and resources continues to increase, and as new technologies are developed to address the technical and environmental challenges associated with it.
Overall, subsea mining is a complex and rapidly evolving industry that has the potential to play a significant role in meeting the growing demand for minerals and resources. However, it is important for subsea mining operations to be conducted in a safe, environmentally responsible, and economically viable manner in order to ensure long-term success.











Simply wish to say your article is as astounding. The clearness in your post is simply great and i could assume you’re an expert on this subject. Well with your permission let me to grab your feed to keep up to date with forthcoming post. Thanks a million and please carry on the enjoyable work.