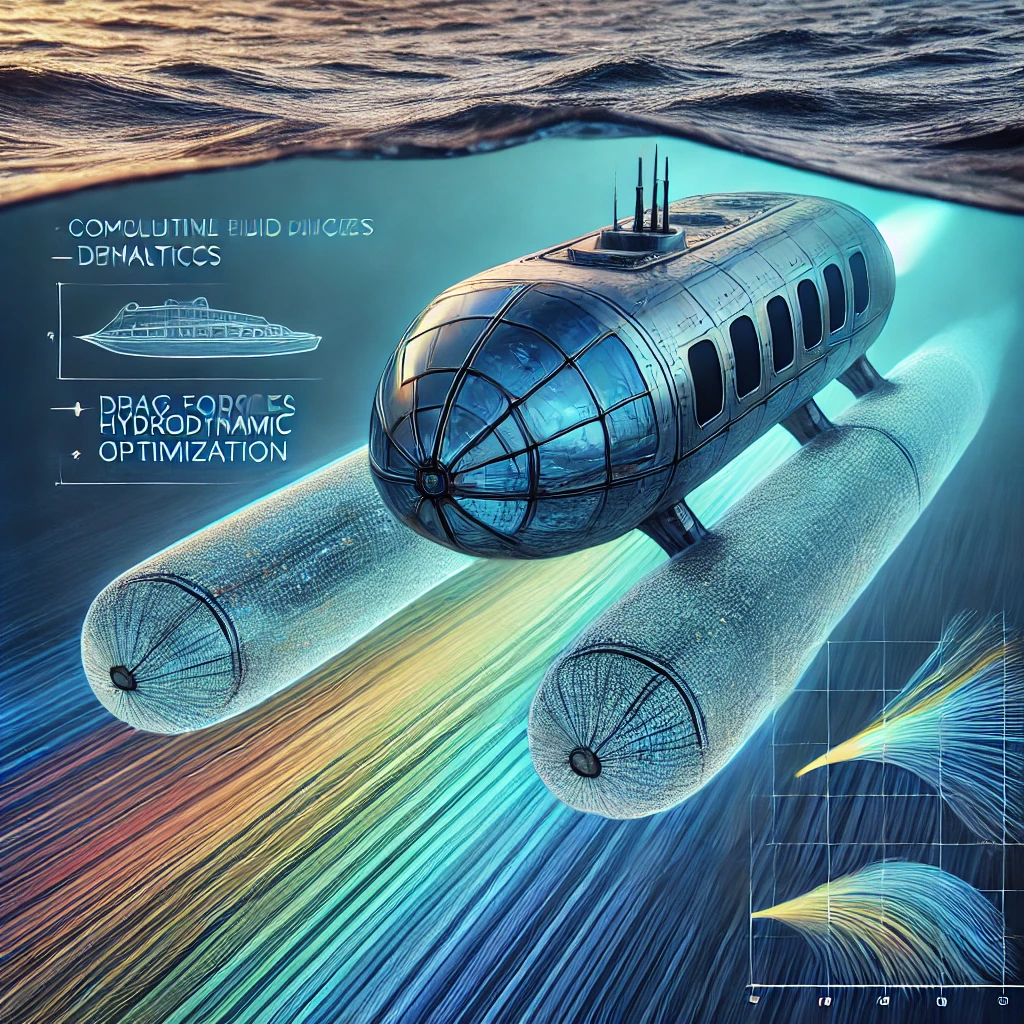
A motor operated valve (MOV) is a special kind of valve that gets controlled by an electric motor. The motor turns a shaft that’s connected to the valve, making it open or close depending on how the motor is positioned. We find these valves commonly in big industries and businesses to manage the flow of liquids like water, air, and steam. They’re really helpful in controlling pressure, temperature, and how fast the fluids move. You’ll often see them in places like heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems, power plants, chemical plants, and other big factories.
A motor operated valve (MOV) is made up of two parts: a valve assembly and an electric actuator. People sometimes call them On-Off valves because the electric motor is responsible for opening and closing them. These valves are mainly used to control the flow of liquids and to stop the flow completely when needed.
Working of a Motor Operated Valve
A motor operated valve (MOV) works with the help of an electric motor to open and close the valve. This motor is connected to the valve’s stem, and when it’s activated, it moves the closure element of the valve, like a ball or gate, to control the flow of fluid through the valve. To make all this happen, there’s a controller that manages the electric motor. This controller can be a simple switch, a programmable logic controller (PLC), or a more advanced process control system. The controller sends signals to the motor based on what flow rate is desired, and it also takes feedback from sensors that keep an eye on the system’s pressure, temperature, and flow rate. All of this together ensures the valve operates smoothly and efficiently.
The Different Types of Motor Operated Valves:
Motor operated valves (MOV) come in three main categories, depending on the type of flow control they achieve:
- Open/Close Valves: These valves are used for regular on-off services. They simply open or close the valve completely, without any in-between positions.
- Inching Valves: Valves which provide some degree of control are called inching valves. They can be adjusted to different positions to control the flow partially.
- Precision Flow Valves: These offer precise control over the flow. They allow for very accurate adjustments to achieve the desired flow rate.
Furthermore, there are various types of motor-operated valves available:
- Quarter-turn valves: These valves require a quarter-turn of the valve stem to open or close fully. Ball valves and butterfly valves are examples of this type.
- Multi-turn valves: These valves need multiple turns of the valve stem to open or close entirely. Globe valves and gate valves fall into this category.
- Linear valves: These valves use linear motion to open and close. Diaphragm valves and pinch valves are examples of linear valves.
- Electric valves: These valves are operated by an electric motor and are commonly used in HVAC systems and other industries.
- Smart valves: These valves have additional features like sensors, communication capabilities, and self-diagnostic capabilities.
The choice of motor-operated valve depends on the specific application and the type of fluid being controlled. Different valves are used to suit the specific needs of each situation.
Versatile Applications in Diverse Industries
Motor operated valves (MOVs) have a wide range of applications in both industrial and commercial settings. Some of the key uses include:
- HVAC Systems: Motor operated valves are used in heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems to manage the flow of air, water, and steam, ensuring proper temperature control and ventilation.
- Power Plants: In power generation systems, MOVs are employed to control the flow of water and steam, which is crucial for the efficient operation of power plants.
- Process Control: Various industries, such as oil and gas, chemical, and food and beverage, rely on MOVs to regulate the flow of liquids and gases during their manufacturing processes.
- Water Treatment: MOVs are essential in municipal and industrial water treatment systems, where they control the flow of water to ensure proper treatment and distribution.
- Fire Protection: In fire suppression systems, MOVs play a vital role in controlling the flow of water during emergencies, helping to extinguish fires effectively.
- Mining: In mining operations, MOVs are used to manage the flow of liquids and gases, contributing to the smooth operation of mining processes.
- Pharmaceuticals: The pharmaceutical industry utilizes MOVs to control the flow of liquids and gases during the production of pharmaceutical products, ensuring accuracy and consistency.
- Automation: MOVs are integrated into automation systems to precisely control the movement of machine parts and other equipment, enhancing the efficiency of various processes.
Overall, wherever there is a need for precise flow control, and manual operation is not practical or possible, MOVs find their applications in diverse industries and processes.
Air Operated Valve vs Motor Operated Valve
Air-operated valves (AOVs) and motor operated valves (MOVs) are both types of actuated valves, meaning they are controlled by an external power source rather than by manual operation. However, there are some important distinctions between the two:
- Power Source: AOVs are powered by compressed air, while MOVs are driven by electricity.
- Speed of Operation: AOVs can open and close more rapidly compared to MOVs because compressed air is more responsive than an electric motor.
- Size and Weight: AOVs are typically smaller and lighter than MOVs because they don’t require an electric motor.
- Cost: AOVs are generally more cost-effective than MOVs since they don’t need the additional components, like the electric motor and control system, that MOVs require.
- Maintenance: AOVs need regular maintenance to ensure that the compressed air supply is clean and dry. MOVs generally require less maintenance, although occasional servicing of the electric motor and control system might be necessary.
- Safety: AOVs are generally considered safer as they don’t require electricity, while MOVs need a power supply, necessitating electrical safety precautions.
When deciding between AOVs and MOVs, various factors such as the specific application, the environmental conditions, the budget, and the safety requirements should be carefully considered to make the most appropriate choice.
Typical Datasheet for a Motor-Operated Valve
A typical datasheet for a motor operated valve (MOV) contains essential details to help users understand and select the right valve for their needs:
- Valve Type and Size: It specifies the type of valve (like ball valve, butterfly valve, or globe valve) and its size (e.g. 3″ NPT).
- Valve Body Material: The material used for the valve body, trim, seat, and sealing components will be mentioned.
- Pressure and Temperature Ratings: It states the maximum pressure and temperature that the valve can handle safely.
- Flow Characteristics: The datasheet provides information about the valve’s flow characteristics, such as Cv (flow coefficient) or Kv (flow factor).
- Actuator Type and Size: This section mentions the type of electric actuator (like rotary or linear) and its size (e.g. 24V DC or 110V AC).
- Control Signal: The type of control signal required to operate the valve, such as 4-20mA, 0-10V, or 24V DC, will be specified.
- Power Consumption: The power consumption of the valve is mentioned, which is important for electrical considerations.
- Ambient and Fluid Temperature Range: The range of temperatures within which the valve can be safely used is provided.
- Enclosure Protection Level: The level of protection offered by the valve’s enclosure against elements like dust and moisture will be detailed.
- Certifications: If the valve has any relevant certifications, such as UL, CE, or ATEX, they will be listed.
- Dimensions and Weight: The datasheet includes the overall dimensions and weight of the valve.
- Valve End Connections: It specifies the valve end connections, like ASME B16.5 (FF, RF, RTJ, Threaded), ASME B16.47 Series A or B, MSS SP-44, ASME B16.25 (BW, SW, WE).
- Other Information: Additional details may be provided, such as recommended spare parts, maintenance schedule, and warranty information.
Remember, the specific information in the datasheet may vary depending on the manufacturer and the particular model of the valve.
Symbols used for Motor Operated Valve(MOV)
The symbol for a motor operated valve (MOV) is a graphical representation used to indicate that the valve is controlled by an electric motor. The symbol typically consists of a circle with the letter “M” inside, along with an arrow pointing in the direction of flow. The arrow demonstrates the flow direction when the valve is open, while the circle with an “M” represents the electric motor responsible for controlling the valve.
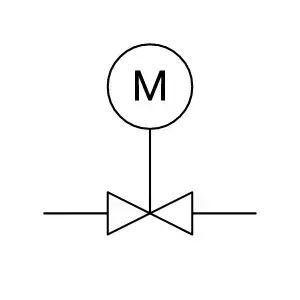
Motor operated valves are widely utilized in various industrial processes to manage the flow of liquids and gases. They find common applications in HVAC systems, power plants, and other industrial environments, where they help regulate pressure, temperature, and flow rate. In engineering diagrams like Piping and Instrumentation Diagrams (P&IDs), the motor-operated valve symbol is used to represent these valves accurately, providing engineers with a clear understanding of the process and aiding in the design of control systems.
Understanding Differences between a Control Valve and a Motor Operated Valve
Control valves and motor-operated valves (MOV) both serve the purpose of controlling fluid flow in a system, but they have some important distinctions:
- Actuation: Control valves offer better control capabilities and are designed for precise adjustments. They are not typically used for simple on-off services. On the other hand, MOVs rely on an electric motor to open and close the valve, making them more suitable for basic on-off control.
- Control Response: Control valves generally respond faster to control signals compared to MOVs.
- Control Elements: Control valves, also, often use analog control elements to regulate flow, pressure, or temperature, while Motor operated valves employ digital control elements.
- Control System Type: Control valves are commonly used in closed-loop systems where precise control is required. In contrast, motorized valves are frequently utilized in open-loop systems.
- Type of Control: Control valves can be employed for various control tasks like pressure, flow, or temperature control. In contrast, motor-operated valves are primarily used for flow control applications.
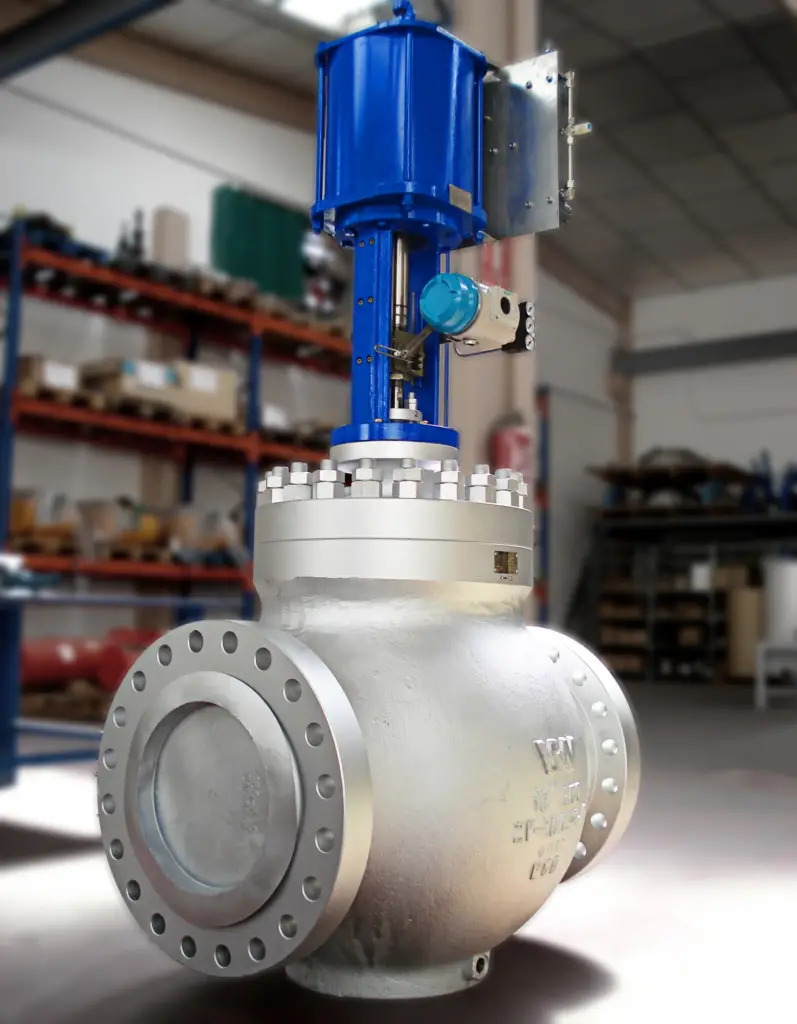

In summary, control valves are ideal for more complex control systems requiring precision, while motor-operated valves are better suited for simpler on-off control tasks in less intricate setups.
Motor Operated Valve Manufacturers
There are numerous reputable manufacturers of motor-operated valves (MOVs) worldwide, each offering a wide selection of valves for various industries and uses. Some of the well-known manufacturers include:
- Emerson: This is a global technology and engineering company that provides a diverse range of MOVs for different industries and applications.
- Flowserve: A prominent provider of flow control products and services, offering a variety of Motor operated valves tailored to industries like oil and gas, chemical, and power generation.
- Rotork: A UK-based company known for designing and manufacturing MOVs suited for a wide range of industries and applications.
- Auma: A German manufacturer specializing in electric actuators and MOVs designed for various industrial purposes.
- Honeywell: A multinational conglomerate offering a range of MOVs suitable for different industries and applications.
- Biffi: An Italian company that designs and manufactures MOVs catering to a wide range of industrial applications.
- Festo: A German manufacturer providing both pneumatic and electric actuators and MOVs for diverse industries and applications.
- Neles: A global provider of flow control solutions primarily for the oil and gas, chemical, and other process industries which produces good quality motor operated valves.
While these are some of the major players, it’s important to note that many other companies also produce motor operated valves to cater to the diverse needs of various industries and applications.