Material Test Certificate, also known as Mill Test Certificate (MTC), is a popular quality assurance document used in the metals industry. While purchasing steel pipes, plates, bars, or other steel materials, the manufacturer provides the material test certificate along with the products that certify the material’s technical specifications. It covers parameters like chemical composition, manufacturing routes, mechanical and physical properties, heat treatment details, testing results, heat traceability, or compliance with a set of international or local standards. In a nutshell, Material Test Certification is considered the ID of a particular material heat and production batch. It indicates its provenance, its quality and can offer insight into material performance under real-life service conditions.
Material Test Certificates (MTCs) play a crucial role in verifying the quality and specifications of steel materials. However, understanding the details can be challenging for buyers. In this article, we will explore the importance of MTCs, discussing how they provide essential information about material composition, manufacturing processes, and compliance with standards. Clear comprehension of Material Test Certificate aids informed decision-making and ensures the desired material quality.
Demystifying the Material Test Certificate
A Material Test Certificate, commonly known as a Mill Test Certificate, is a document issued by the manufacturer to confirm that a product aligns with the specified chemical and mechanical properties. This certification, often presented in paper form, is also referred to as a material test report. It includes essential information such as factory quality control approval and is typically stamped with a special material test certificate mark. It’s important to note that not all commercially available materials require a material certificate. Nevertheless, when provided, the Material Test Certificate serves as a vital assurance of product quality and compliance with industry standards.
Decoding the Contents of a Material Test Certificate
Material test certificates can vary between manufacturers, but they generally provide the following details:
- Certificate Type and Standard: Specifies the type of certificate (e.g., EN 10204 3.1 or EN 10204 3.2) and the applicable standard.
- Manufacturer Information: Includes the name of the manufacturer, product name, weight, and dimensions.
- Material Heat Number: Identifies the specific heat and production batch of the material.
- Quantity Covered: Indicates the quantity of the material covered by the certificate.
- Batch Number: Physical marking on the product, corresponding to the batch mentioned in the certificate.
- Chemical Composition Analysis: Provides the results of the analysis, detailing the composition of the material.
- Mechanical Test Results: Includes mechanical properties such as tensile strength, yield strength, etc.
- Dimensional Measurement Results: Verifies compliance with dimensional tolerances specified in the standard, including parameters like diameter, wall thickness, length, and straightness (specific to steel pipes).
- Material Grade and Specification: Specifies the material grade (e.g., A106-B) and the relevant specification, along with the results of chemical and mechanical tests.
- Additional Test Results: Reports any supplementary tests conducted, such as hydrostatic, ultrasound (UT), magnetic particle, metal graphics, hardness, impact tests, etc.
- Addenda: Any additional information that helps evaluate the complete characteristics of the product.
It’s important to note that the reference standards for testing and report content typically align with the manufacturing facility’s standards or the specific requirements of the clients.
Exploring the Different Types of Material Test Certificates (Mill Test Certificates)
These test certificates are commonly issued in accordance with the EN 10204 standard. Under this standard, there are four distinct types of Material Test Certificates:
- MTC Type 2.1: This type of certificate confirms that the material meets the specified requirements based on non-specific inspection and testing by the manufacturer.
- MTC Type 2.2: This certificate includes additional information compared to Type 2.1. It verifies that the material meets the specified requirements based on specific inspection and testing carried out by the manufacturer.
- MTC Type 3.1: This certificate is endorsed by an independent inspection agency. It confirms that the material meets the specified requirements after thorough inspection, testing, and verification of the manufacturing process.
- MTC Type 3.2: Similar to Type 3.1, this Material Test Certificates is also endorsed by an independent inspection agency. It includes additional examination and testing, such as witnessing the production process and conducting additional non-destructive testing on the material.
These different types of Material Test Certificates provide varying levels of assurance regarding the material’s compliance with specified standards and quality requirements. Let us talk about these certificates in more details.
Material Test Certificate Type 2.1
A Material Test Certificate 2.1 is a document that signifies that the supplied products meet the requirements specified in the order. However, unlike other types of certificates, Material Test Certificates 2.1 does not include detailed test results. Instead, it serves as a declaration from the manufacturer or supplier that the materials conform to the specified standards, without providing specific data on the testing performed.
MTC 2.1 is typically used when the client’s requirements focus on verifying the overall compliance of the materials without necessitating detailed test reports. While it confirms that the products meet the necessary standards, it lacks the specific test results that would provide further insight into the material’s properties or performance.
Material Test Certificate Type 2.2
In a Material Test Certificate 2.2, the manufacturer affirms that the supplied products meet the requirements specified in the order. Unlike Material Test Certificate 2.1, this certificate includes the test results within the report. The testing results are obtained through a non-specific inspection conducted by the manufacturer themselves, allowing them to determine the tests without external guidance or prescribed requirements.
MTC Type 2.2 distinguishes itself from Material Test Certificates Type 2.1 by providing specific test results, which offer more detailed information about the material’s properties and characteristics. These results contribute to a more comprehensive understanding of the product’s compliance with the specified standards and order requirements.
By presenting the test results, Material Test Certificates 2.2 offers greater transparency and accountability regarding the quality and performance of the supplied materials.
Material Test Certificate Type 3.1
The issuance of a Material Test Certificate 3.1 involves the manufacturer providing a formal declaration that the supplied products fully comply with the order requirements. This certificate goes beyond just confirming compliance; it also includes the results of the necessary tests as specified by the product specification, official regulations, and relevant rules.
To ensure impartiality, the document must be validated by an authorized inspection representative appointed by the manufacturer. This representative acts independently of the manufacturing department, adding an additional layer of credibility to the certificate.
By combining a declaration of compliance with verified test results, Material Test Certificate 3.1 provides customers with comprehensive assurance regarding the quality, conformity, and performance of the supplied products.
Material Test Certificate Type 3.2
In the case of Material Test Certificate 3.2, validation can be carried out by either the manufacturer’s authorized inspection representative (independent of the manufacturing department), the purchaser’s authorized inspection representative, or a third-party inspector.
With MTC 3.2, the manufacturer declares that the supplied products meet the requirements of the received order. The certificate includes test results, similar to MTC 3.1. However, a significant distinction is that MTC 3.2 necessitates the report to be countersigned by an independent inspection authority. This sets it apart from MTC 3.1, where validation is conducted solely by a company representative independent of the manufacturing process.
Both MTC 3.1 and 3.2 require the producer to implement traceability procedures and furnish relevant inspection documents when requested. These certificates play a crucial role in ensuring compliance, quality, and traceability throughout the manufacturing and supply process.
Deciphering the Material Test Certificate
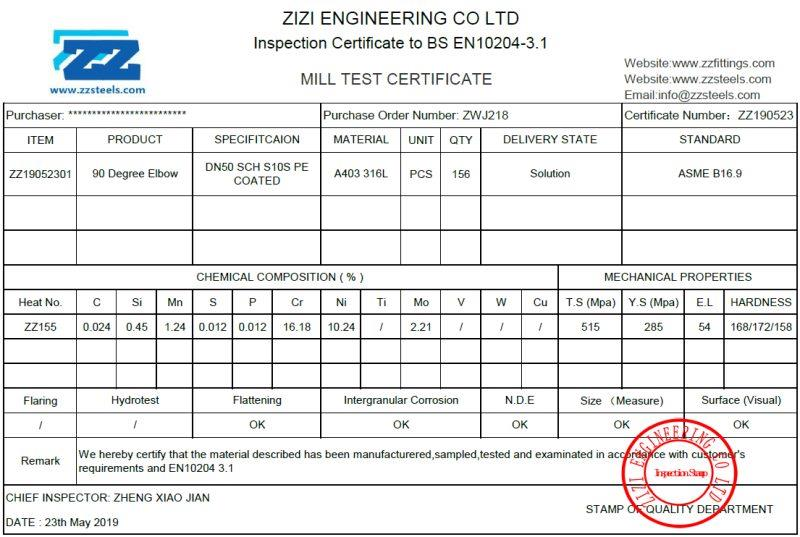
Understanding the contents of a material test certificate can be challenging at times. To simplify the process, let’s examine a sample material test certificate and explain the essential information it provides. By focusing on the following details, you can gain a clearer understanding:
1. Name of the manufacturer
At the top section of a material test certificate, you will find the name of the manufacturer responsible for producing the product. In the given example, the company name and their address are clearly mentioned. Typically, a Material Test Certificate includes important manufacturer details such as the company name, logo, country of origin, and workshop location. This information serves to identify and establish the source of the certified material, ensuring transparency and accountability in the supply chain.
2. Lot Number/Material Heat Number/Cast Number
In a Material Test Certificate (MTC), it is crucial to include the lot number or material heat number, as it serves as the primary means of traceability for the specific material. The lot number or heat number mentioned on the certificate must match the one assigned to the corresponding metal product. This ensures accurate identification and tracking throughout the supply chain.
The lot number plays a vital role in connecting the mechanical and chemical properties of the material with its corresponding heat number. By linking these properties to the lot number, proper identification and verification of the material become possible, ensuring that it meets the required specifications and standards.
3. Material Grade and Specification
The grade and specification of the material are provided, which outline its chemical, mechanical, and physical properties. For instance, the MTC may indicate a dual-certified stainless steel TP 316/316L, specifying the material grade and composition.
4. Delivery Condition:
The MTC confirms the delivery condition of the material, indicating details such as whether it is welded (RT or UT), seamless (SMLS), or welded with specific testing requirements (e.g., 100% RT or UT).
MTC includes abbreviated forms in the report as follows:
- W – Welded (RT or UT)
- SMLS – Seamless
- WX – Welded (100% RT)
- WU – Welded (100% UT)
5. Material Dimensions
The dimensions of the product are mentioned, varying depending on the type of material. For example, in the case of a plate, the dimensions may include length, width, thickness, and weight.
6. Weight of the Material:
The MTC specifies the weight of the material per unit length. Some of the material’s price also depends on the weight of the product.
7. Mechanical Properties:
The Material Test Certificate includes mechanical properties such as strength, hardness, and elongation, providing insight into the material’s performance and compliance with the purchase order requirements.
8. Chemical Analysis:
The chemical composition of the material, determined through analysis corresponding to the heat number, should match the required element specifications stated in the purchase order.
9. Heat Treatment:
If applicable, the MTC mentions any specific heat treatment processes that the material has undergone.
10. Hydrotest and Non-Destructive Testing Requirements:
This section lists the details of tests performed, including hydrostatic testing and non-destructive examination, when applicable.
11. Supplementary:
Any additional information relevant to the material, such as results of a positive material identification (PMI) test or compliance with NACE standards, may be included.
12. Certified Mill Signature:
A material test certificate must be signed and stamped by authorized personnel, indicating the authenticity and accuracy of the information provided.
Understanding these components of a Material Test Certificate helps in evaluating the material’s quality, compliance, and suitability for its intended use.
Purpose of Material Test Certificate
Verification of Product Quality
Material Test Certificates (MTCs) play a crucial role in certifying the quality of a product. They serve as a guarantee that the product has undergone the necessary testing procedures and meets the required standards. It is essential for the MTC to be provided along with the product to ensure transparency and accountability.
By verifying the product’s quality through a Material Test Certificate, customers can have confidence in the material’s suitability for their intended use. It provides assurance that the product has been thoroughly tested and meets the required standards, reinforcing trust and facilitating informed decision-making.
Improved Transparency and Traceability
Material Test Certificates (MTCs) not only certify the quality of a product but also offer transparency and traceability throughout the manufacturing process. By referring to the material test certificate associated with each heat number, it becomes effortless to trace specific materials.
MTCs enhance transparency by providing documented evidence of the manufacturing process, test results, and compliance with standards. This ensures that the materials have undergone rigorous testing and meet the specified requirements. Moreover, MTCs include vital information like heat numbers, enabling easy identification and tracking of individual materials.
This transparency and traceability offered by MTCs promote quality control, facilitate product verification, and simplify material identification during production and distribution. By leveraging the information provided in the certificates, stakeholders can confidently trace and verify the origin and characteristics of specific materials, ensuring a reliable and accountable supply chain.